Gravitational Wave Network



Planned Lifetime: 2028+
End of Operations: No specific requirement
Data Archive: GW Open Science Center
LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA comprise the advanced gravitational wave detector network. LIGO is operated by the National Science Foundation, Virgo by the European Gravitational Wave Observatory, and KAGRA by the ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology-Japan (MEXT). Together they detect, localize, and characterize the coalescence of compact binary mergers, continuous gravitational waves, and burst gravitational waves.
| Interferometers | Location | Size | Joined GW Network | BNS Range (O4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
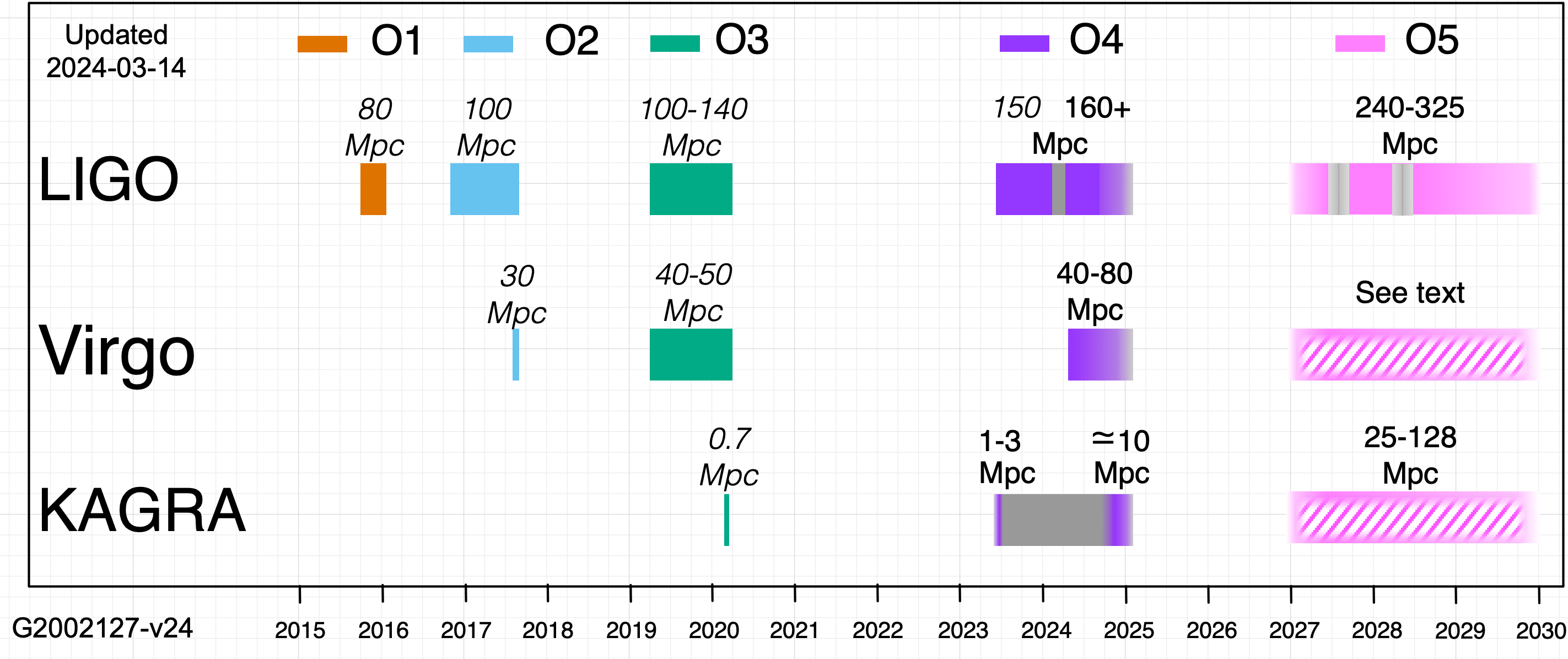
| Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) | Hanford, WA, USA Livingston, LA, USA | 4 km | 2015 | 160-190 Mpc |
| Virgo Gravitational Wave Interferometer (Virgo) | Pisa, Italy | 3 km | 2017 | 90-120 Mpc |
| Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) | Kamioka-cho, Hida-city, Gifu-prefecture, Japan | 3 km | 2020 | 25-230 Mpc |
GCN Notice Types in GCN Classic and GCN Classic Over Kafka: Detailed Descriptions and Examples
| Type | Contents | Latency |
|---|---|---|
LVC_EARLY_WARNING | A pre-merger alert. | -1-0 minutes |
LVC_PRELIMINARY | First Notice, Timestamp Alert, location probability sky map; all automated processing. | 1–10 minutes |
LVC_INITIAL | Improved SkyMap now available (human-involved processing). | 4–24 hours |
LVC_UPDATE | Ultimate refined sky map (more detailed off-line processing). | ~1–7 days |
LVC_RETRACTION | After human analysis/evaluation, a retraction will be issued if trigger is not astrophysical. | 1 hour–1 day |
Common GCN Circular Types:
| Type | Latency | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Identification of a GW trigger | 4-24 hours | LIGO/Virgo S191105e |
| Updated sky localization of a GW trigger | 1-7 days | LIGO/Virgo S191105e |
| Retraction of a GW trigger | 1 day | LIGO/Virgo S191117j |
Predicted Annual Detection Rates for O4:
| Merger Class | Detection Rates per Calendar Year | Area [deg2] |
|---|---|---|
| Binary Neutron Star | 10 (0–62) | 33 (28–38) |
| Neutron Star-Black Hole | 1 (0–92) | 50 (42–58) |
| Binary Black Hole | 79 (35–168) | 41 (35–48) |
O4 predictions from Abbott et al. 2020, LRR. Uncertainties are the 90% confidence interval, including Poisson uncertainty. This document is updated periodically for future observing runs.